Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board or PCB is a cost-effective, fast, tidy, compact and resilient way to manufacture electronic circuitry.
Description
Circuit pathways are etched out of a thin sheet of copper on a hard board, rather than being formed from individual loose wires; these pathways are referred to as "traces". A sealant layer is placed over the top of the copper; traditionally, this layer was green or brown, but bright colours are often seen now, red in particular.
Circuit components are soldered onto printed circuit boards. On a typical single-sided PCB, the components are placed onto one side, and the copper circuit traces are placed on the other. Many PCBs have copper traces on both sides to permit more complex circuitry to be arranged. The components may have legs that are pushed through holes punched in the PCB, or they may simply have small metal contacts, and be glued in place before being soldered; the latter approach is called "surface mount", and is commonly used for small components such as resistors and light-emitting diodes.
Switch mount
In mechanical keyboards, the individual switches are all soldered onto a printed circuit board. Some switches are supported by the PCB alone, but better keyboards will include a sheet steel plate to support the switches. The exact method by which the switches are held in place is referred to as the switch mount.
PCB-mounted Cherry MX Blue switches
PCB-mounted Cherry MX Blue switches
Plate-mounted Simplified Alps Type IV switches
Membrane keyboards only require a small PCB, to support the keyboard controller and connect to the membrane
Examples
Section of the circuit design schematic for the Phantom
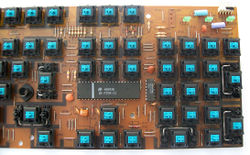
Alps Electric-made PCB in an Apple M0116 keyboard
A batch of HID Liberation Device boards fresh from manufacturing
Complex controller and feature PCB from the Cherry G80-9013 phoneboard
Bright red PCB for the trackball in a Marquardt Military Keyboard
Manufacturers
Notable PCB manufacturers include: